Host discovery with TCP
Split port scans by port number
Low TCP port scans
Medium TCP port scans
High TCP port scans
Split scans
Split the scans to get a set of results back in a shorter period of time. This makes it possible to start testing while the remaining results come back. By the time medium port scans are finished, underlying services of the lower ports have probably been enumerated.
Use ports 0-1024 for the low range (System Ports). These scans cover services such as SMTP, Windows File Sharing, HTTP, HTTPS and other commonly found services.
For medium port use ports 1025-32767 (the bulk of the User Ports). These cover NFS, Sun RPC Port Mapper, X-Windows, VNC, Microsoft Terminal Services, etc.
The high port scans are for ports in the range 32768-65535 (the lesser used User Ports and Dynamic or Ephemeral ports).
Hints
Do not ping the target in these scans because there may be filtering in place, which could result in pings failing and nmap accidentally concluding that a host is down.
Under the hood
TCP SYN (Stealth) scan (-sS) is the default and most popular scan option for good reason. It can be performed quickly,
scanning thousands of ports per second on a fast network not hampered by intrusive firewalls. SYN scan is relatively
unobtrusive and stealthy, since it never completes TCP connections. It works against any compliant TCP stack, and
allows clear, reliable differentiation between open, closed, and filtered states.
Nmap starts by sending a TCP packet with the SYN flag set and the target send back a response with the SYN and ACK flags. NMap does not complete the handshake with the expected ACK and the OS suddenly receives a SYN/ACK while it hasn’t requested (NMap did). The OS responds to the unexpected SYN/ACK with an RST packet. All RST packets in such scenarios also have the ACK bit set because they are always sent in response to (and acknowledge) a received packet.
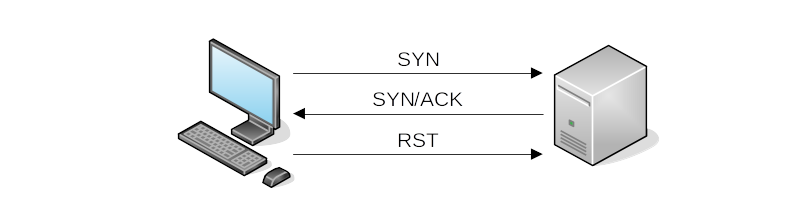
Because the three-way handshake is never completed, SYN scan is sometimes called half-open scanning.
If a service is listening on a port and someone makes a connection to it (by sending a
SYNpacket), the service will send aSYN/ACKpacket in return. That means that there is a machine at that IP address. Note that some operating systems will respond with aSYN/ACKtoSYNs sent to ports used for outbound TCP connections, while others will not.If no service is listening on that port but the machine is up and running and on the network, a reset (
RST) packet will be sent back. That means there is nothing listening on that port, but having sent something in return means that a machine is at that IP address.If nothing is received after sending a
SYNpacket, it means there is no host at that IP address OR a firewall is blocking traffic OR the host is down. Port 80 is therefore extremely useful for ping sweeps, because most firewalls and port filters do not block web traffic.
| Send | Receive | Send | Assumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYN | SYN/ACK | ACK followed by RST | Port is open, host is up |
| SYN | RST | - | Port is closed, host is up |
| SYN | Nothing | - | Port is blocked by firewall, host is down, or there is no host at that IP address. |
Interpreting portscan outputs
Some puzzling with indicators will help:
Anything from 40000 onwards could be anything and only be temporary
NFS can run on any port, but the Linux NFS Kernel server implementation always runs on port 2049 by default.
VNC clients typically are on port 5900+ If port 5900 AND 5901 are open, most likely 5901 is a second VNC service. If port 5901 is open and 5900 closed, who knows?
TCP port 8080 open can indicate a proxy server, or something like Apache Tomcat, or …
A Windows Active Directory controller will have TCP ports 53 (DNS), 88 (Kerberos), 389 (LDAP), 636 (LDAP/S) and the common NetBIOS and Windows File Sharing ports 135 (used for RPC comms for AD replication), 139 (Authentication) and 445 (used for a whole host of services including file sharing and authentication)
Windows systems tend to use TCP port 3389 for Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol access.
Unix-like systems often use text-based protocols on TCP ports 22 (SSH), 23 (Telnet) and 514 (RSH), or network-based Windowing protocols on TCP ports such as 590x (VNC) or 600x (X11).
Examples
Low TCP port scans:
# nmap -sS -PN -p 0-1024 -n -iL $TARGETFILE -oA nmap/tcp-lo
The result is an open port list, with port and protocol, the port’s state and the by IANA allocated service for that port. This does not mean that a port actually runs that service.
Medium TCP port scans:
# nmap -sS -PN -p 1025-32767 -n -iL $TARGETFILE -oA nmap/tcp-med
Remaining TCP port scans:
# nmap -sS -PN -p 32768-65535 -n -iL $TARGETFILE -oA nmap/tcp-hi
Expect to find Sun RPC services or DCE RPC services, 3rd-party backup utilities, and application services with SAP deployments.